What is Phishing ?

Phishing is the attempt to obtain sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details (and sometimes, indirectly, money), often for malicious reasons, by masquerading as a trustworthy entity in an electronic communication.
Phishing emails may contain links to websites that are infected with malware.
Phishing is typically carried out by email spoofing or instant messaging, and it often directs users to enter details at a fake website whose look and feel are almost identical to the legitimate one.
Phishing is an example of social engineering techniques used to deceive users, and exploits the poor usability of current web security technologies.
Attempts to deal with the growing number of reported phishing incidents include legislation, user training, public awareness, and technical security measures.
Many websites have now created secondary tools for applications, like maps for games, but they should be clearly marked as to who wrote them, and users should not use the same passwords anywhere on the internet.
Phishing is a continual threat, and the risk is even larger in social media such as Facebook, Twitter, and Google+.
Hackers could create a clone of a website and tell you to enter personal information, which is then emailed to them.
Hackers commonly take advantage of these sites to attack people using them at their workplace, homes, or in public in order to take personal and security information that can affect the user or company (if in a workplace environment).
environment).
Phishing takes advantage of the trust that the user may have since the user may not be able to tell that the site being visited, or program being used, is not real; therefore, when this occurs, the hacker has the chance to gain the personal information of the targeted user, such as passwords, usernames, security codes, and credit card numbers, among other things.
Types of Phishing Attacks
Numerous different types of phishing attacks have now been identified. Some of the more prevalent are listed below.
Deceptive Phishing. The term phishing originally referred to account theft using instant messaging but the most common broadcast method today is a deceptive email message. Messages about the need to verify account information, system failure requiring users to re-enter their information, fictitious account charges, undesirable account changes, new free services requiring quick action, and many other scams are broadcast to a wide group of recipients with the hope that the unwary will respond by clicking a link to or signing onto a bogus site where their confidential information can be collected.
Malware-Based Phishing refers to scams that involve running malicious software on users PCs. Malware can be introduced as an email attachment, as a downloadable file from a web site, or by exploiting known security vulnerabilitiesa particular issue for small and medium businesses (SMBs) who are not always able to keep their software applications up to date.
software applications up to date.
Keyloggers and Screenloggers are particular varieties of malware that track keyboard input and send relevant information to the hacker via the Internet.
They can embed themselves into users browsers as small utility programs known as helper objects that run automatically when the browser is started as well as into system files as device drivers or screen monitors.
Session Hijacking describes an attack where users activities are monitored until they sign in to a target account or transaction and establish their bona fide credentials.
At that point the malicious software takes over and can undertake unauthorized actions, such as transferring funds, without the users knowledge.
Web Trojans pop up invisibly when users are attempting to log in.
They collect the users credentials locally and transmit them to the phisher.
Hosts File Poisoning. When a user types a URL to visit a website it must first be translated into an IP address before its transmitted over the Internet.
The majority of SMB users PCs running a Microsoft Windows operating system first look up these host names in their hosts file before undertaking a Domain Name System (DNS) lookup. By poisoning the hosts file, hackers have a bogus address transmitted,taking the user unwittingly to a fake look alike website where their information can be stolen.
System Reconfiguration Attacks modify settings on a users PC for malicious purposes.
For example: URLs in a favorites file might be modified to direct users to look alike websites.
For example: a bank website URL may be changed from bankofabc.com to bancofabc.com.
Data Theft. Unsecured PCs often contain subsets of sensitive information stored elsewhere on secured servers.
Certainly PCs are used to access such servers and can be more easily compromised. Data theft is a widely used approach to business espionage.
By stealing confidential communications, design documents, legal opinions, employee related records, etc., thieves profit from selling to those who may want to embarrass or cause economic damage or to competitors.
DNS-Based Phishing (Pharming). Pharming is the term given to hosts file modification or Domain Name System (DNS)-based phishing.
With a pharming scheme, hackers tamper with a companys hosts files or domain name system so that requests for URLs or name service return a bogus address and subsequent communications are directed to a fake site.
The result: users are unaware that the website where they are entering confidential information is controlled by hackers and is probably not even in the same country as the legitimate website.
Content-Injection Phishing describes the situation where hackers replace part of the content of a legitimate site with false content designed to mislead or misdirect the user into giving up their confidential information to the hacker.
For example, hackers may insert malicious code to log users credentials or an overlay which can secretly collect information and deliver it to the hackers phishing server.
Man-in-the-Middle Phishing is harder to detect than many other forms of phishing.
other forms of phishing.
In these attacks hackers position themselves between the user and the legitimate website or system.
They record the information being entered but continue to pass it on so that users transactions are not affected.
Later they can sell or use the information or credentials collected when the user is not active on the system.
Search Engine Phishing occurs when phishers create websites with attractive (often too attractive) sounding offers and have them indexed legitimately with search engines.
Users find the sites in the normal course of searching for products or services and are fooled into giving up their information.
For example, scammers have set up false banking sites offering lower credit costs or better interest rates than other banks.
Victims who use these sites to save or make more from interest charges are encouraged to transfer existing accounts and deceived into giving up their details.


 This is when someone looks through your files in the hopes of finding something interesting whether it is electronic or on paper.
This is when someone looks through your files in the hopes of finding something interesting whether it is electronic or on paper.




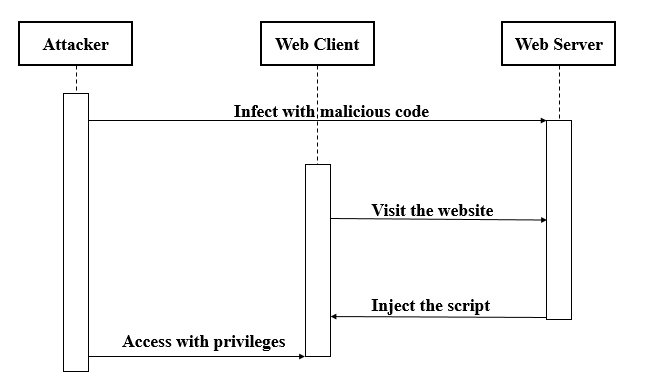
 RFI tricks existing software on your webpage to access malicious code elsewhere on the internet and to execute it with privileges.
RFI tricks existing software on your webpage to access malicious code elsewhere on the internet and to execute it with privileges.